Project Management (CMMI-DEV)
Summary
Project Management (CMMI-DEV) process areas cover the project management activities related to planning, monitoring, and controlling the project.
Description
The seven Project Management process areas in CMMI-DEV are as follows:
- Integrated Project Management (IPM) (CMMI-DEV)
- Project Monitoring and Control (PMC) (CMMI-DEV)
- Project Planning (PP) (CMMI-DEV)
- Quantitative Project Management (QPM) (CMMI-DEV)
- Requirements Management (REQM) (CMMI-DEV)
- Risk Management (RSKM) (CMMI-DEV)
- Supplier Agreement Management (SAM) (CMMI-DEV)
Basic Project Management Process Areas
The Basic Project Management process areas address the activities related to establishing and maintaining the project plan, establishing and maintaining commitments, monitoring progress against the plan, taking corrective action, and managing supplier agreements.
Figure 4.3 provides a bird’s-eye view of the interactions among the Basic Project Management process areas and with other process area categories. As illustrated in Figure 4.3, the Project Planning process area includes developing the project plan, involving relevant stakeholders, obtaining commitment to the plan, and maintaining the plan.
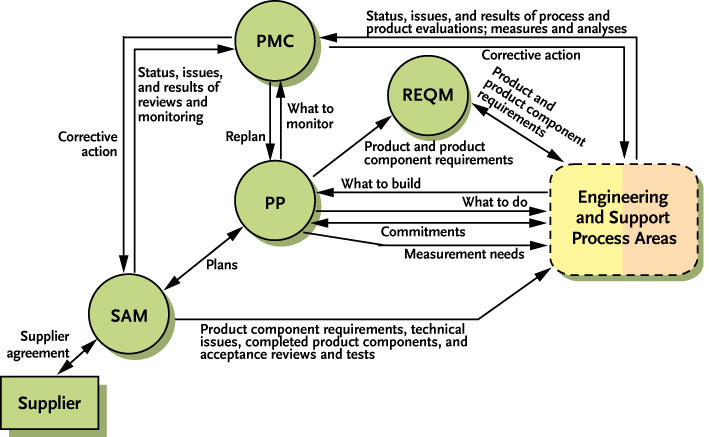
Figure 4.3 Basic Project Management Process Areas
Planning begins with requirements that define the product and project. The project plan covers the various project management and development activities performed by the project. The project reviews other plans that affect the project from various relevant stakeholders and establish commitments with those stakeholders for their contributions to the project. For example, these plans cover configuration management, verification, and measurement and analysis.
The Project Monitoring and Control process area includes monitoring activities and taking corrective action. The project plan specifies the appropriate level of project monitoring, the frequency of progress reviews, and the measures used to monitor progress. Progress is determined primarily by comparing project status to the plan. When the actual status deviates significantly from the expected values, corrective actions are taken as appropriate. These actions may include replanning.
The Supplier Agreement Management process area addresses the need of the project to acquire those portions of work that are produced by suppliers. Sources of products that may be used to satisfy project requirements are proactively identified. The supplier is selected, and a supplier agreement is established to manage the supplier. The supplier’s progress and performance are tracked by monitoring selected work products and processes, and the supplier agreement is revised as appropriate. Acceptance reviews and tests are conducted on the supplier-produced product component.
Advanced Project Management Process Areas
The Advanced Project Management process areas address activities such as establishing a defined process that is tailored from the organization’s set of standard processes, establishing the project work environment from the organization’s work environment standards, coordinating and collaborating with relevant stakeholders, forming and sustaining teams for the conduct of projects, quantitatively managing the project, and managing risk.
Figure 4.4 provides a bird’s-eye view of the interactions among the Advanced Project Management process areas and with other process area categories. Each Advanced Project Management process area depends on the ability to plan, monitor, and control the project. The Basic Project Management process areas provide this ability.
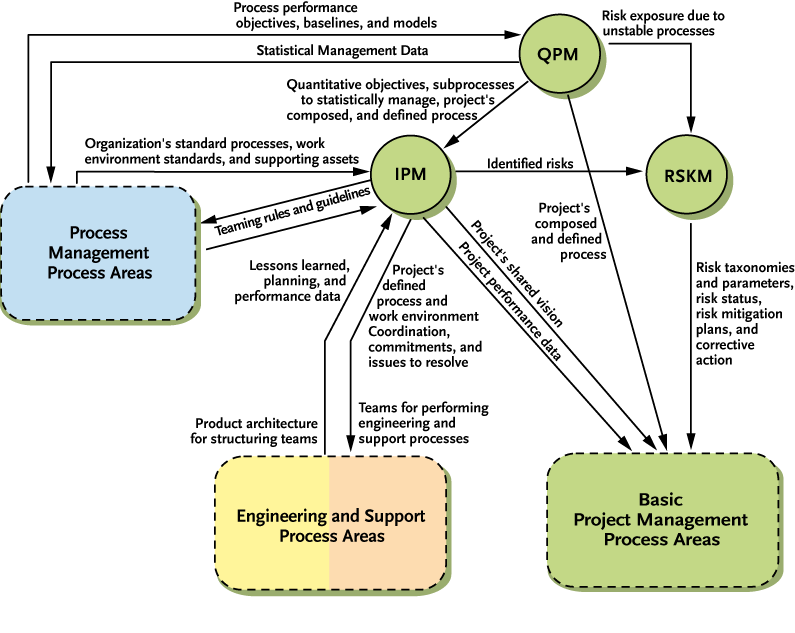
Figure 4.4 Advanced Project Management Process Areas
The Integrated Project Management process area establishes and maintains the project’s defined process that is tailored from the organization’s set of standard processes (Organizational Process Definition). The project is managed using the project’s defined process.
The project uses and contributes to the organizational process assets, the project’s work environment is established and maintained from the organization’s work environment standards, and teams are established using the organization’s rules and guidelines. The project’s relevant stakeholders coordinate their efforts in a timely manner through the identification, negotiation, and tracking of critical dependencies and the resolution of coordination issues.
Although risk identification and monitoring are covered in the Project Planning and Project Monitoring and Control process areas, the Risk Management process area takes a continuing, forward-looking approach to managing risks with activities that include identification of risk parameters, risk assessments, and risk mitigation.
The Quantitative Project Management process area establishes objectives for quality and process performance, composes a defined process that can help achieve those objectives, and quantitatively manages the project. The project’s quality and process performance objectives are based on the objectives established by the organization and the customer.
The project’s defined process is composed using statistical and other quantitative techniques. Such an analysis enables the project to predict whether it will achieve its quality and process performance objectives. Based on the prediction, the project can adjust the defined process or can negotiate changes to quality and process performance objectives. As the project progresses, the performance of selected subprocesses is carefully monitored to help evaluate whether the project is on track to achieving its objectives.
Contains
- Requirements Management (REQM) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Requirements Management (REQM) (CMMI-DEV) is to manage requirements of the project’s products and product…
- Project Planning (PP) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Project Planning (PP) (CMMI-DEV) is to establish and maintain plans that define project activities.
- Project Monitoring and Control (PMC) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Project Monitoring and Control (PMC) (CMMI-DEV) is to provide an understanding of the project’s progress …
- Supplier Agreement Management (SAM) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Supplier Agreement Management (SAM) (CMMI-DEV) is to manage the acquisition of products and services from…
- Integrated Project Management (IPM) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Integrated Project Management (IPM) (CMMI-DEV) is to establish and manage the project and the involvement…
- Risk Management (RSKM) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Risk Management (RSKM) (CMMI-DEV) is to identify potential problems before they occur so that risk handli…
- Quantitative Project Management (QPM) (CMMI-DEV)
- The purpose of Quantitative Project Management (QPM) (CMMI-DEV) is to quantitatively manage the project to achieve the p…
