For our German customers, we have adopted the principles of Lean Startup translated into German - and provided with explanations. Our aim is to convey the meaning of the Lean Startup principles. This is lost in a purely literal translation.
Lean Startup
Lean Startup is a method from the Lean & Agile method set. It helps to develop new product ideas as leanly as possible. The basic idea is to address the greatest uncertainties - and therefore risks - in a new product at an early stage, collect concrete facts and make further decisions based on these facts.
Lean Startup is a child of Agile because it consciously addresses decisions under uncertainty (of which a new product contains many). Agile addresses uncertainty through increments that can be used to gather facts about uncertainties in technology and the market and then base good decisions on these facts. Lean Startup is also a child of Lean because it tries to avoid waste: Namely, the development of products or product features that miss customer needs.
A product can also be a service (e.g. advice). It is often a combination of product and service (e.g. car sharing).
Incidentally, it does not always have to be the launch of a completely new product. Lean Startup also applies to the launch of a new product feature, e.g. the self-driving function on a tractor or a new area for a car-sharing provider.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
In the lean startup method, an increment or concrete result that can be used to collect facts about ambiguities, uncertainties, questions, etc. is called a minimum viable product (MVP).
An MVP is a product that can be used by the customer. This can be a landing page, for example, which is completely manual behind the scenes in order to test hypotheses. The idea is that with an MVP, the actual behavior of users can be observed and validated learning for further development can take place.
The principles of Lean Startup
Lean Startup has five principles that guide its actions. They provide a good outline of the thinking behind the "Lean Startup" method.
1. entrepreneurship is everywhere
No matter what kind of company - large or small - you work for: If a new product is to be created, it is entrepreneurship.
Lean Startup refers to the "startup" of a new product - this has nothing to do with the size of a company. Lean Startup is therefore of interest to anyone who wants to launch a new product (or a new service) on the market: this could be the new café in the city center, a small company with a Kickstarter-product, a new camera from Leica or the new e-car from Volkswagen. Lean Startup is probably a good approach for all of these projects.
2 Entrepreneurship includes management
A new product is not just the product itself, but much more: a business model and an organization, among other things. Entering the market with a new product therefore requires not only entrepreneurship, but also leadership and organizational skills, in short: management.
3 Entrepreneurship involves learning through validation
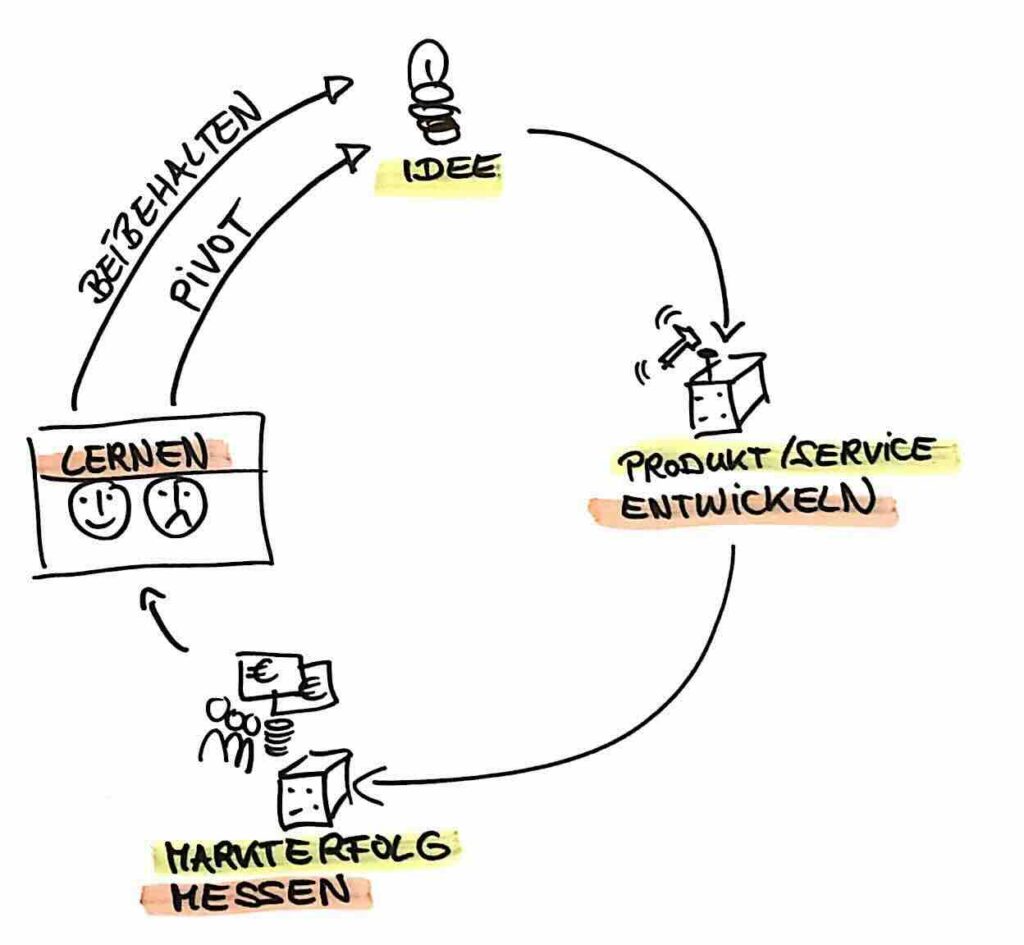
When developing a new business model, we measure progress in the form of validated hypotheses. The greatest value we can generate at the start of a new product is to eliminate the major uncertainties. Will the product be bought? Can we implement the product technically? Can the product be produced economically? These are the three key questions of any new product.
Before we invest large sums in the product, we need fact-based answers to these questions. Because if even one of the questions receives a "no", we must at least radically correct the direction - or stop investing altogether. Lean Startup therefore specifically helps to avoid wasting investment money. In order to have answers to these questions, we formulate hypotheses, build MVPs to validate these hypotheses and learn from the findings.
4 Entrepreneurship involves measuring innovations.
We validate hypotheses with market data. So it's not just about simply learning - it's about facing the market and learning from it. Because only there can the two questions "Will the product be bought?" and "Can the product be produced economically?" be answered.
In order to answer the market questions based on facts, it is important to measure concretely. This could be reservations, as with Tesla's Model 3. It can be purchases, as with Kickstarter. It can be visits to a website. It can be A/B tests.
5 Entrepreneurship involves developing, measuring and learning in short cycles
The first four principles of Lean Startup focus on developing, measuring and learning. We want to do all of this in short cycles: the faster our develop-measure-learn cycles are, the faster we reduce uncertainty and risk. A rhythm helps us to overcome our inner pig dog and face up to learning again and again.

Comments
Write a comment